BPMN Level 2 - Part 2
Medium Scope: Gateways and Iteration
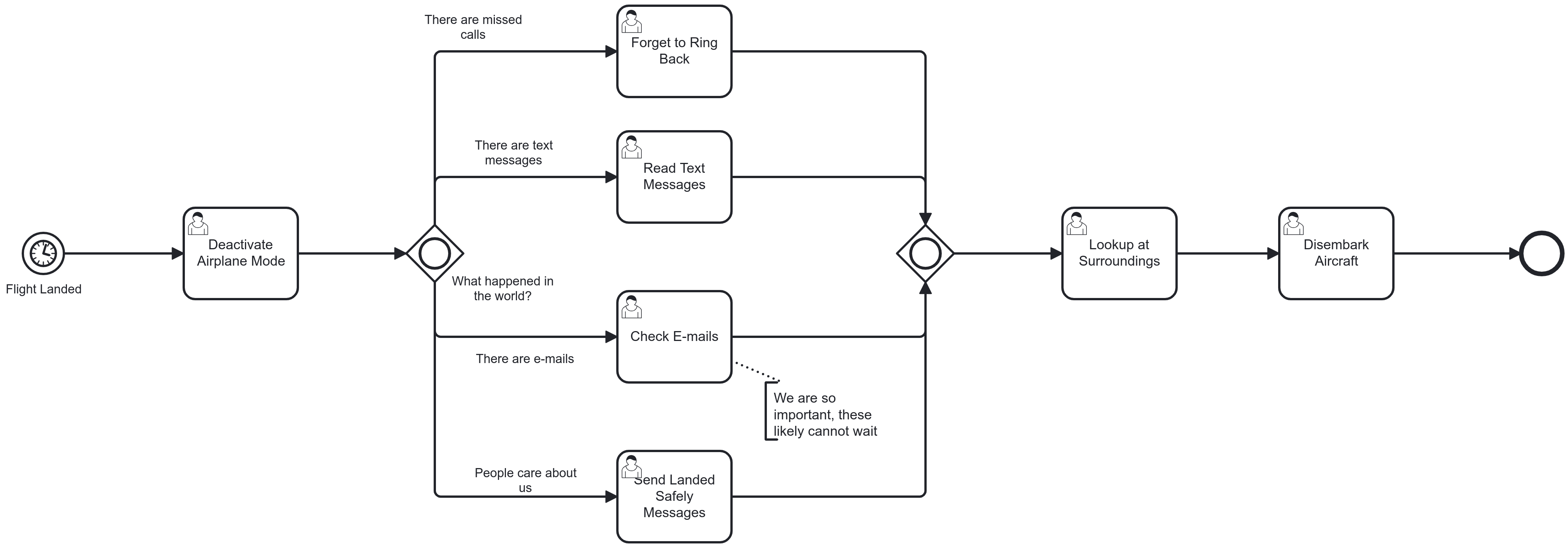
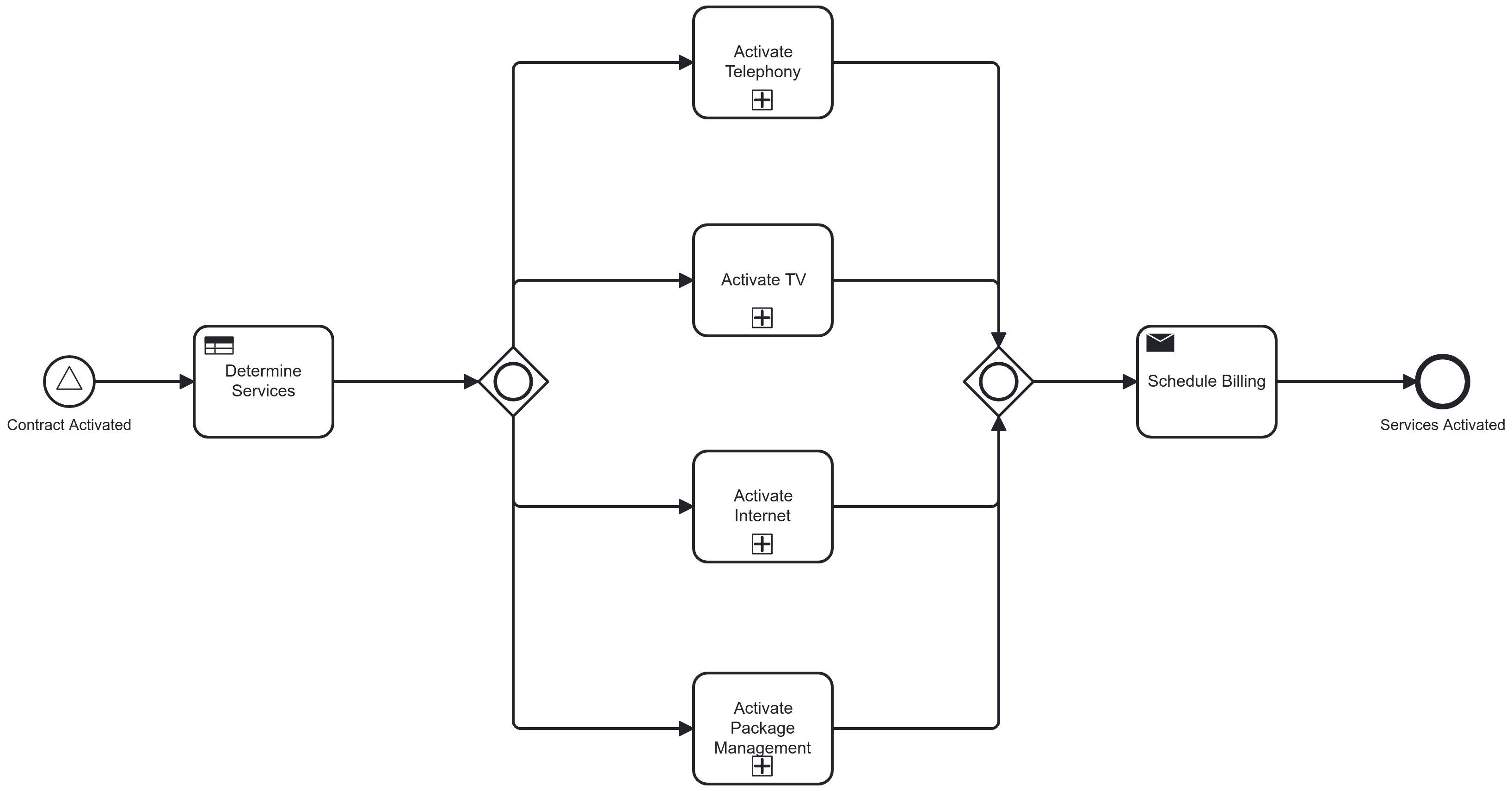
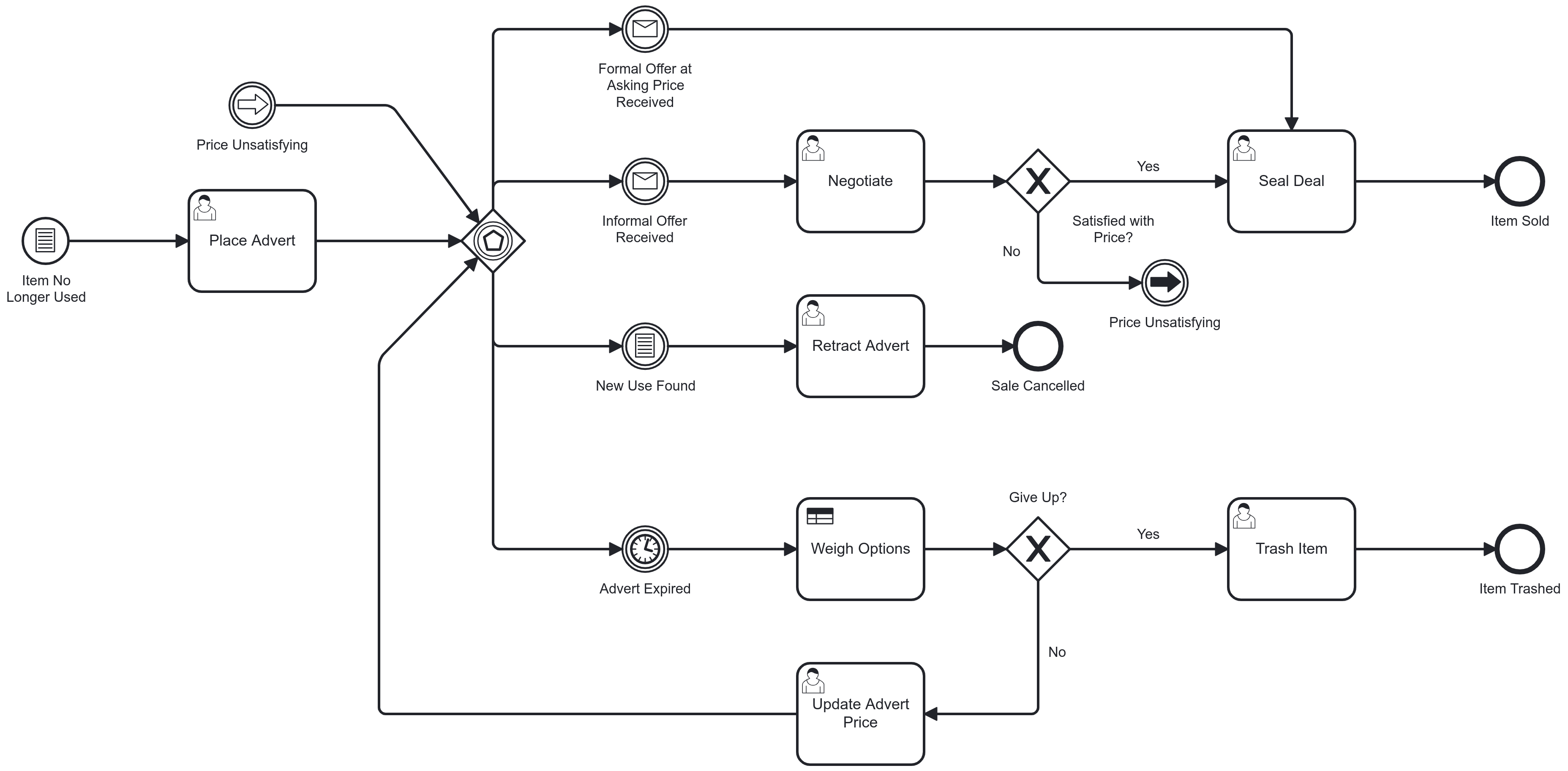
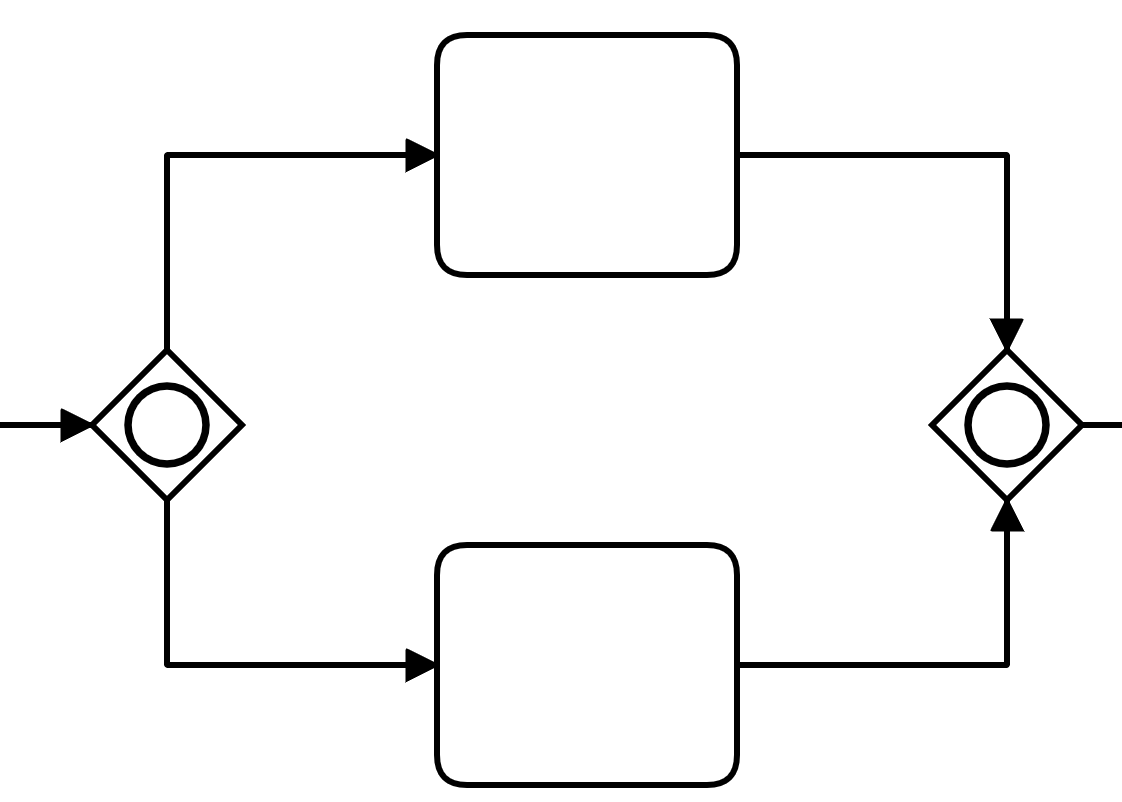
Inclusive Gateway
-
Splits and merges conditionally parallel paths
-
Splitting behaviour: evaluate all conditions of outgoing sequence flow and follow each matching path in parallel
-
Merging behaviour: join all activated incoming sequence flows and proceed after arrival of the last[1]
Default Flow
-
Applies to exclusive and inclusive gateways
-
In diverging (splitting) behaviour
-
-
Default does not mean "by default" or "always", but otherwise
-
Check the conditions of outgoing sequence flows
-
If nothing matches, take the sequence flow marked as default
-
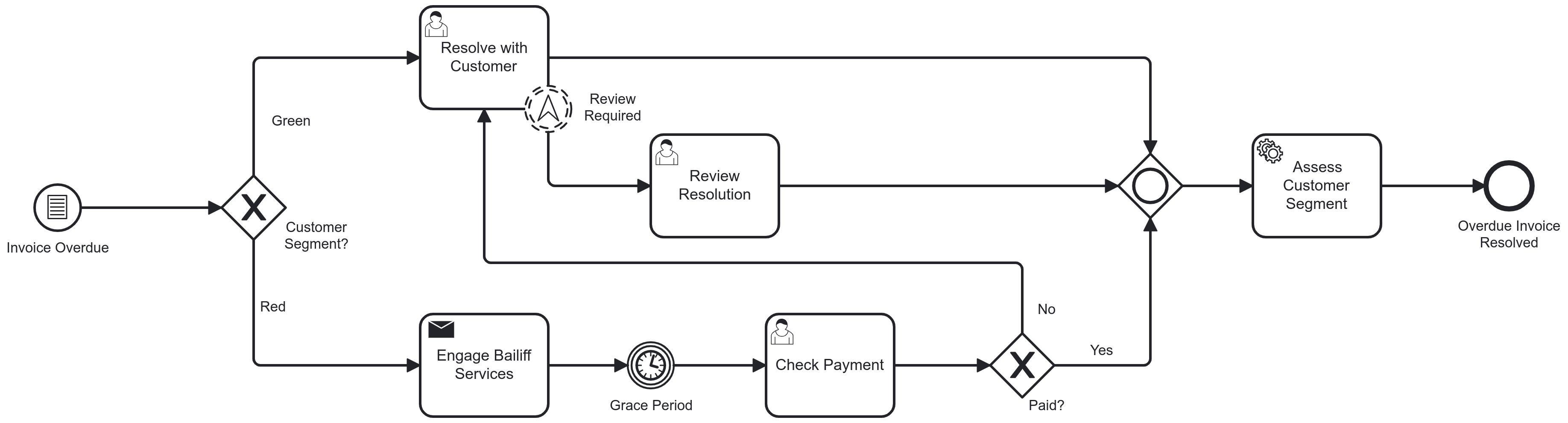
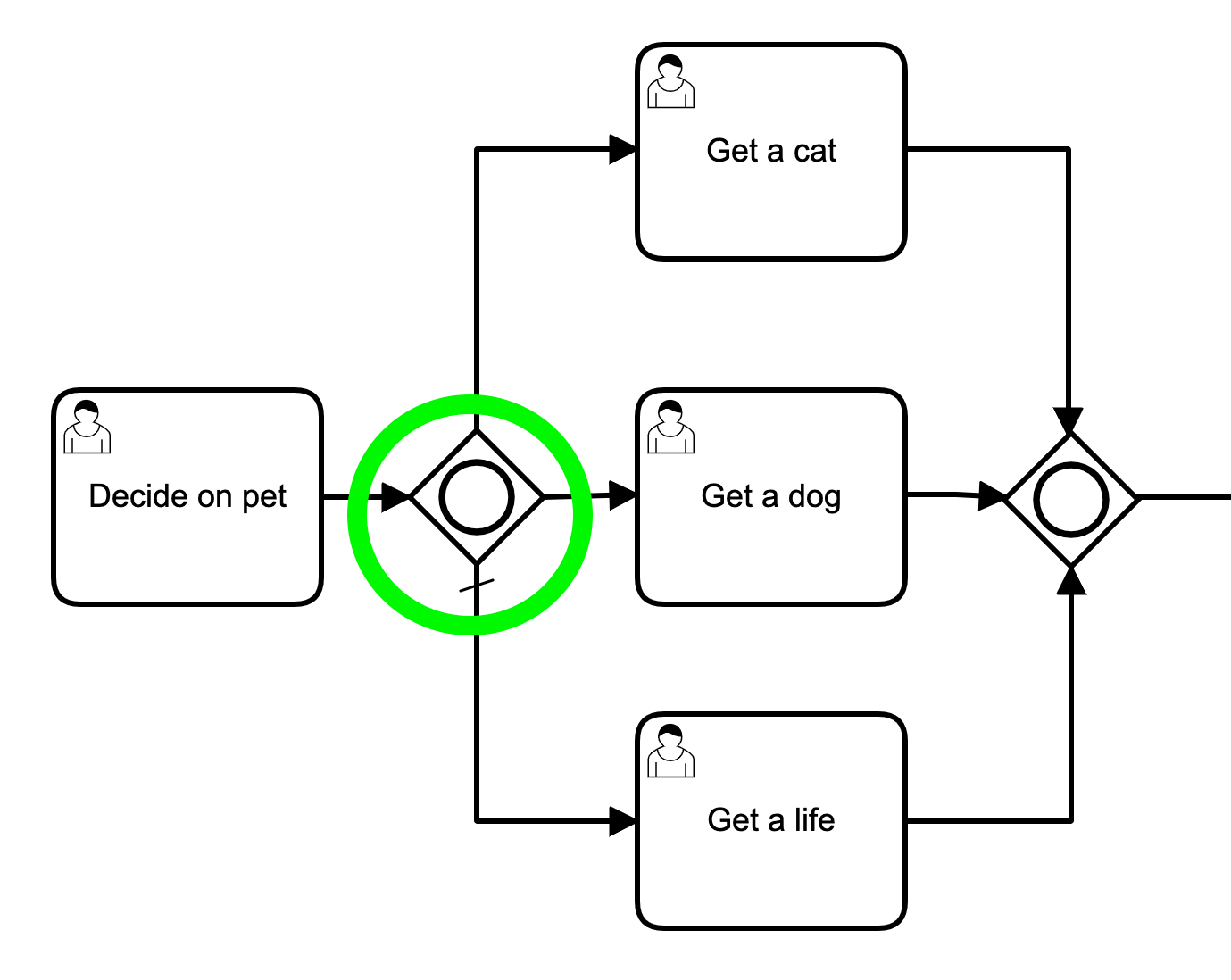
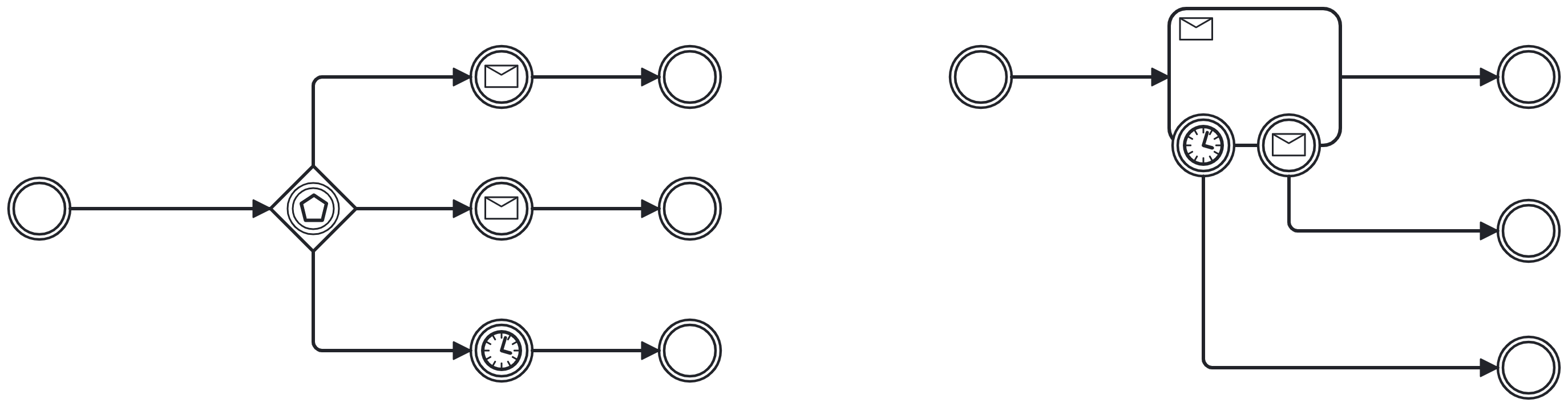
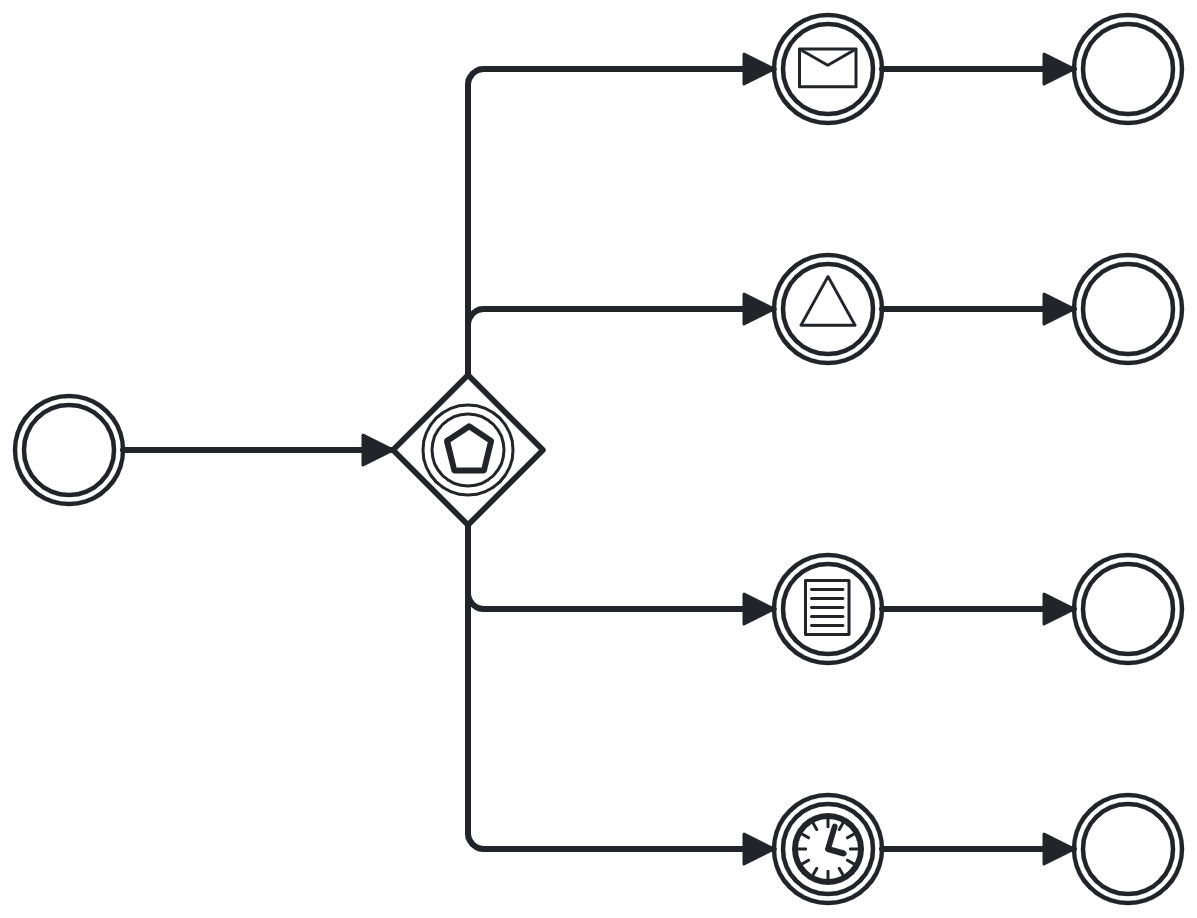
Event Based Gateway
-
Chooses a process path based on the event[2] following the gateway that triggers first
-
Event types allowed:
-
Message
-
Signal
-
Conditional
-
Timer
-
-
Flow continues on the single path leaving the event that fired
-
Only used as diverging gateway, no merge behaviour
Event Based Gateway vs. Receive Task with Boundary Event(s)
-
Some would say, a matter of taste
-
They work the same, but do they mean the same?
-
Primary action vs. equality of actions
-
Use a task for a primary action with exceptions
-
Use a gateway if the various events are more equal (probability, frequency, value, etc…)
-
Iteration
-
BPMN offers various ways to iterate in process models
-
Applied by multiple elements
-
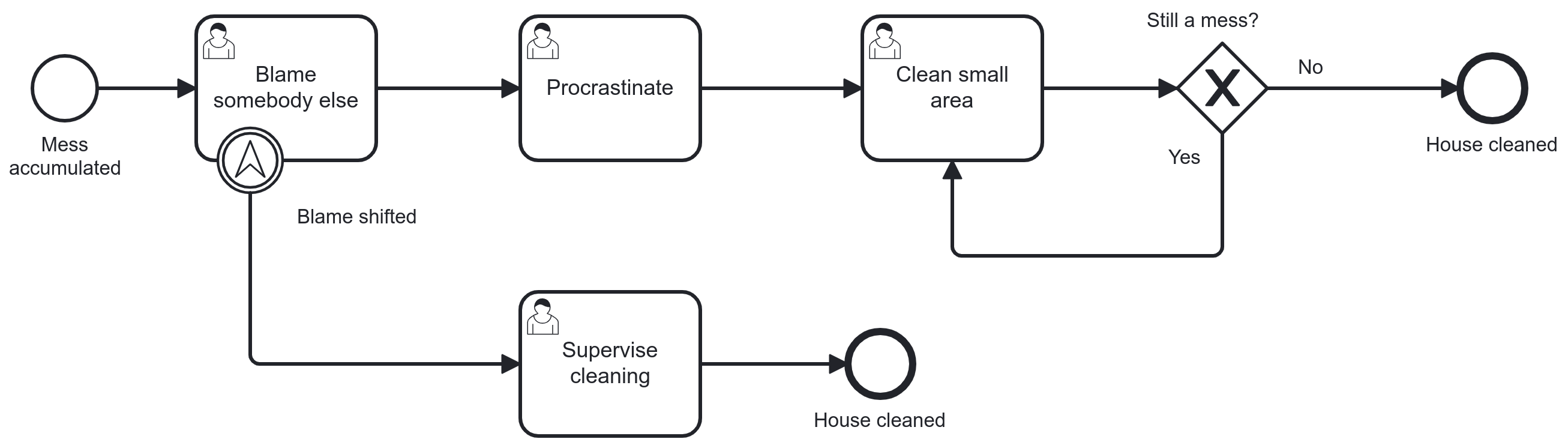
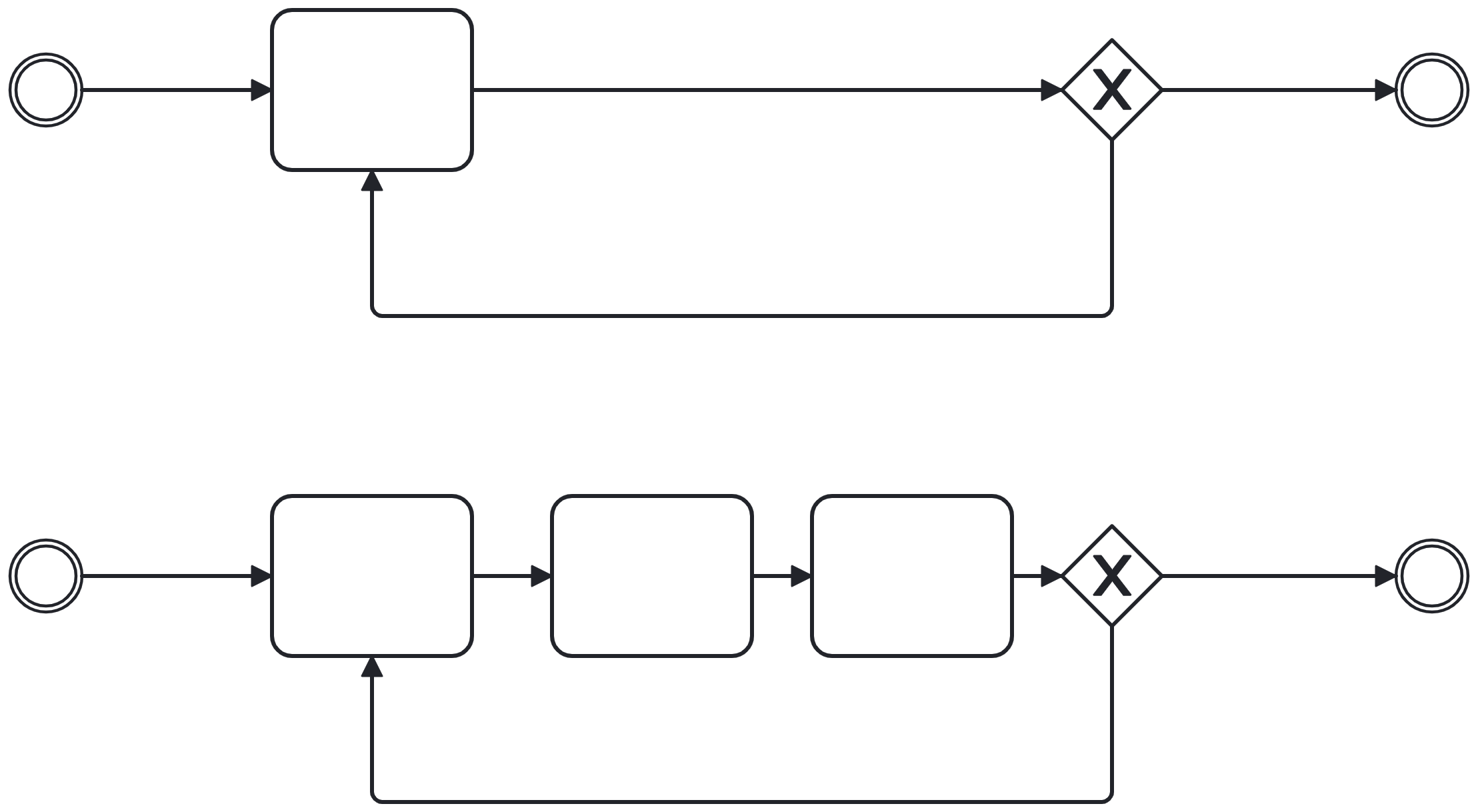
Loop back with control flow
-
-
Applied with single elements
-
Loops (do… while)
-
Multi-instances (for each… do)
-
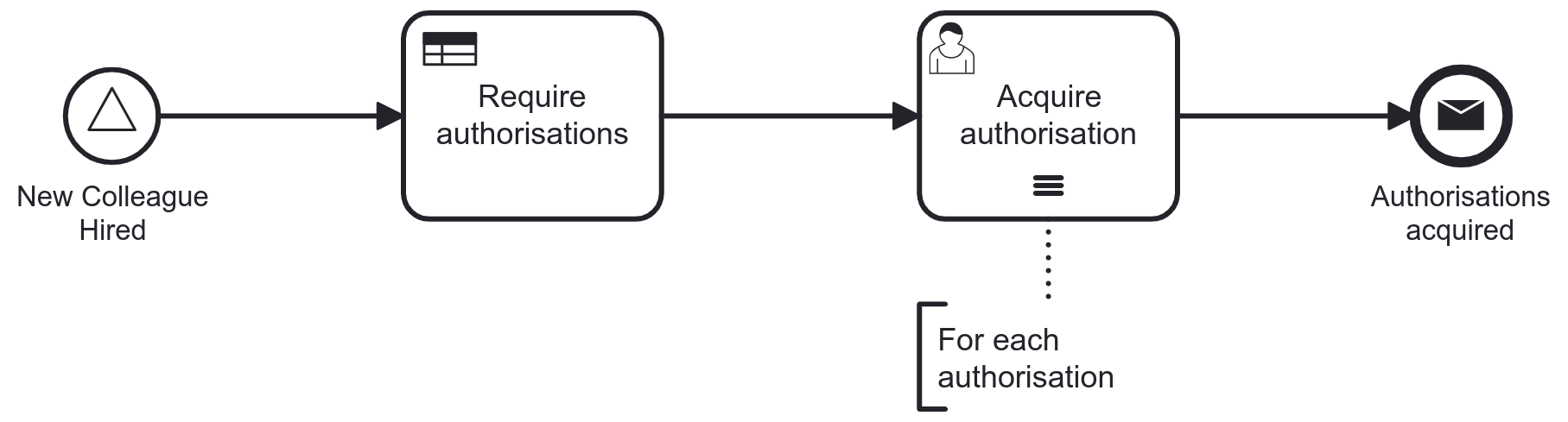
Loop Back with Control Flow
-
Manage the iteration yourself
-
Usually guarded by an exclusive gateway or conditional event (with event subprocess, later)
Loops
-
Loop marker added to activity
-
The number of iterations is unknown upfront: a completion condition determines when the loop stops by turning
false -
Process engine[3] manages the iteration by evaluating the completion condition after each execution
-
Iteration is always sequential: the activity is conditionally repeated
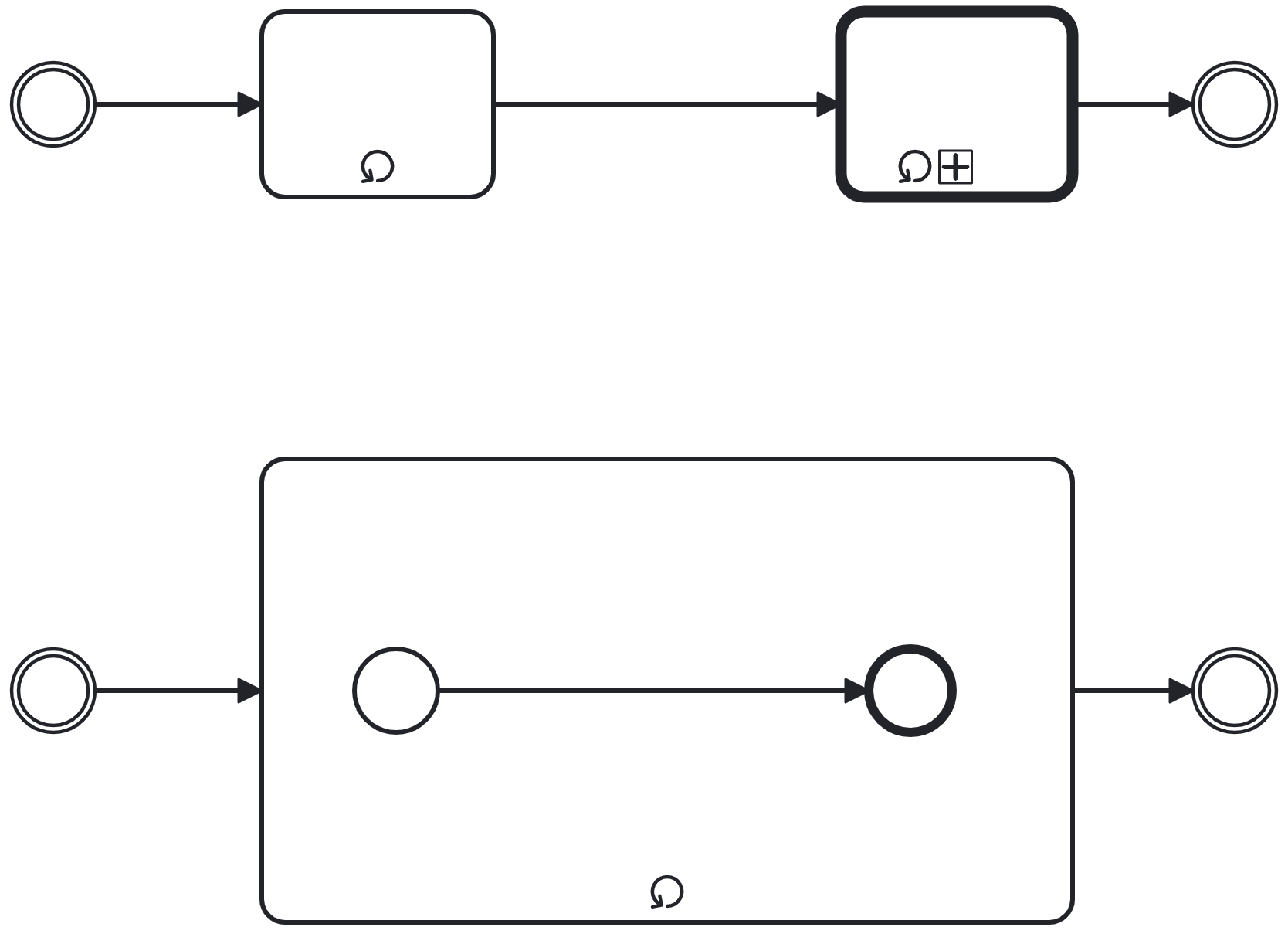
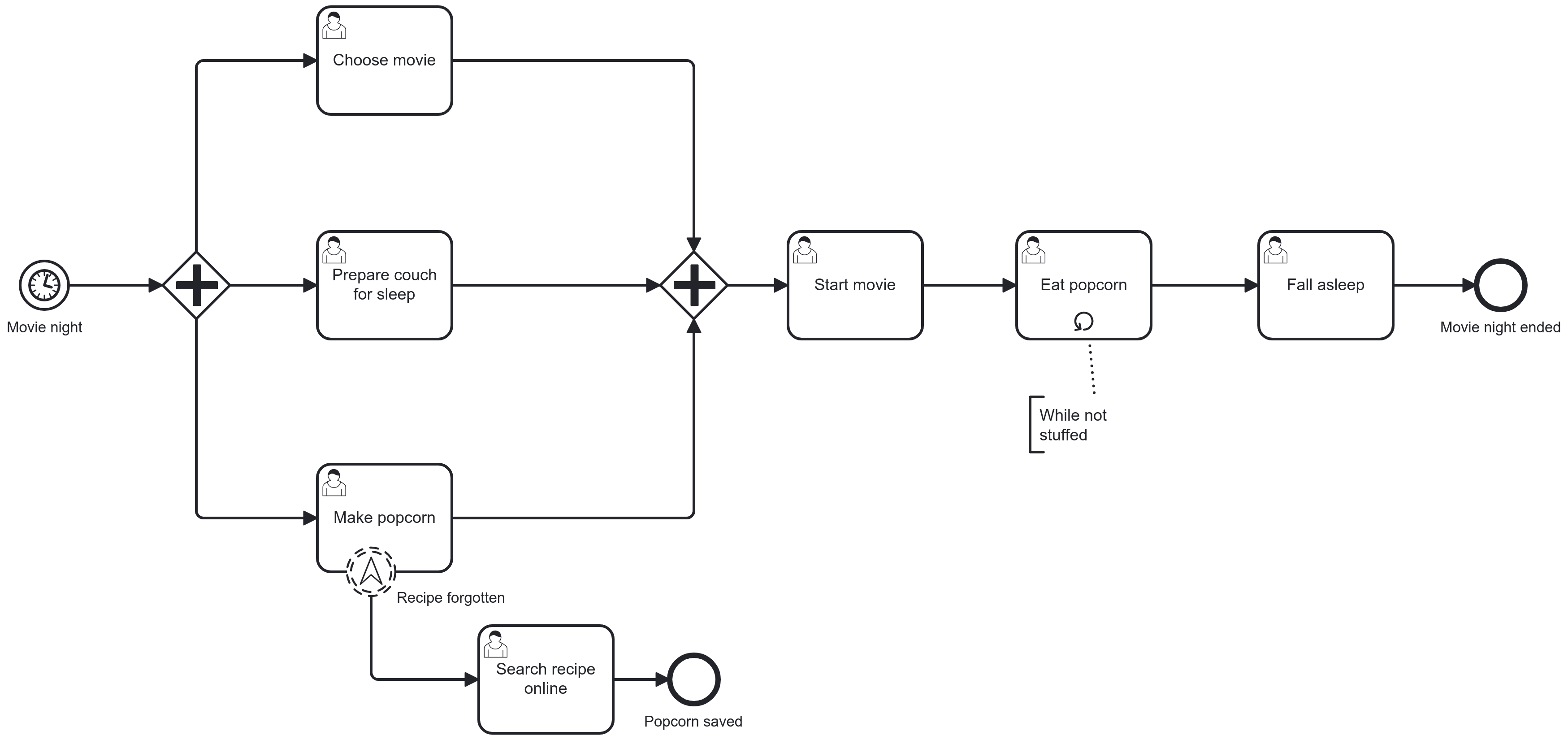
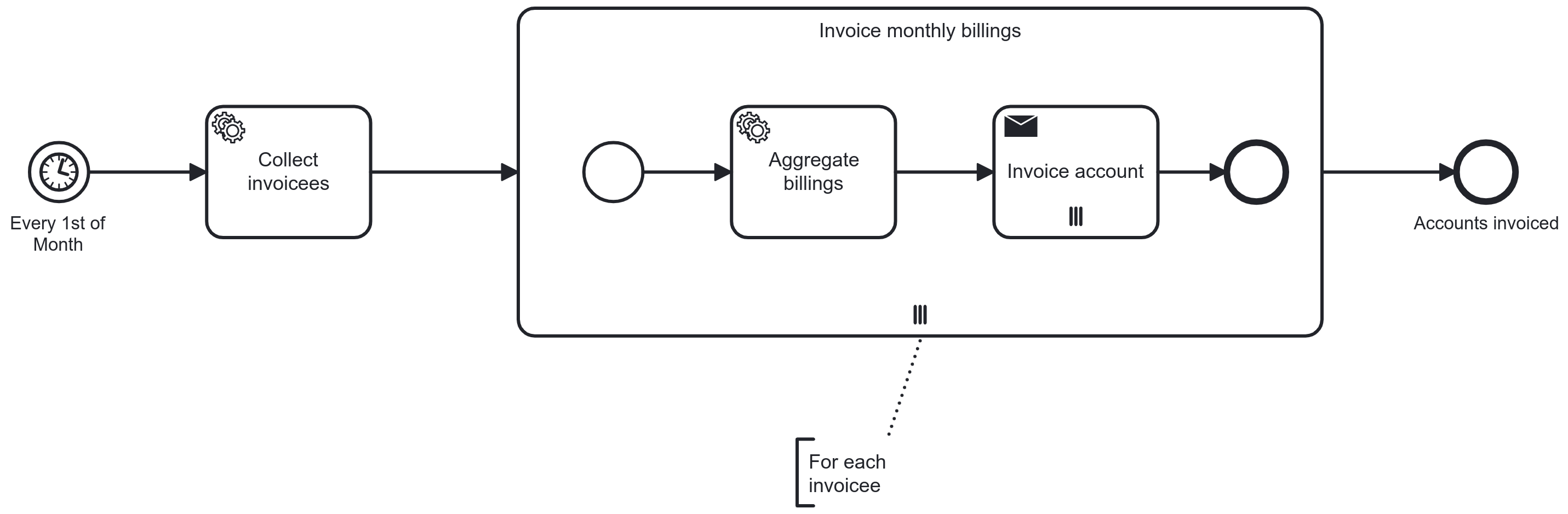
Multi-Instance
-
Multi-instance marker added to activity and/or pool
-
Number of iterations is known upfront: one iteration for each item in a list of the process data
-
Typical use case: collections of sub elements
-
Process engine manages the iteration by executing once for each item
-
Iteration can be sequential or parallel: type of marker determines
-
3 parallel horizontal bars: sequential
-
3 parallel vertical bars: parallel
-
-
The activity completes after all instances have been executed
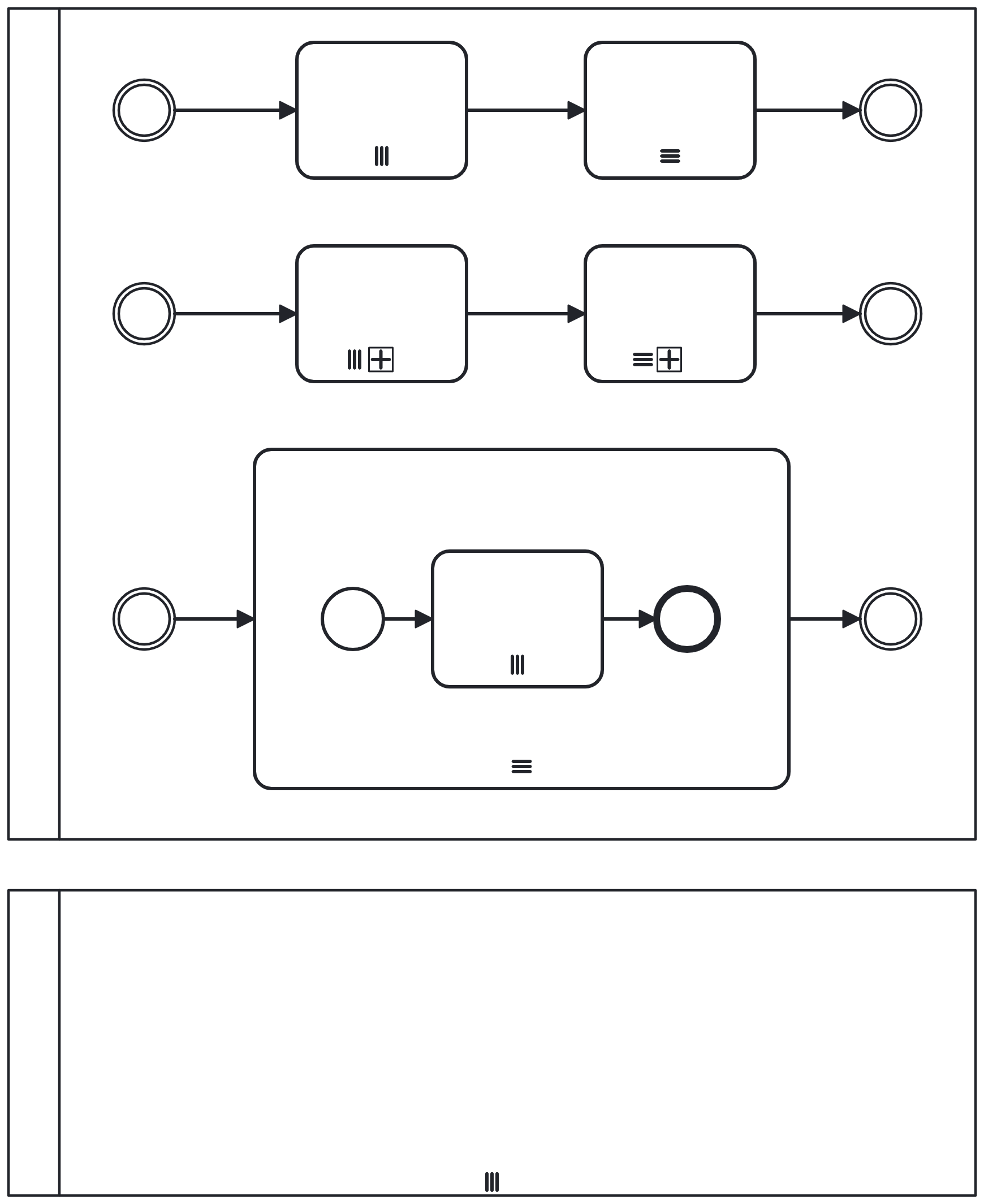
Gateways
-
Consider event-based gateway vs. receive task with boundary events
-
Don’t use names for event-based gateways and converging inclusive gateways: the behaviour is never process specific
-
For diverging inclusive gateway, consider naming as a question with answers on outgoing sequence flows, just like exclusive gateways
-
A business rule task is a natural predecessor to a diverging inclusive gateway
-
Don’t add conditions to sequence flows leaving an event-based gateway
Iteration
-
Always use a text annotation near the iteration marker to indicate the condition or collection
-
Consider using a separate process model for the contents of a multi-instance body because the objects you operate on don’t match 1:1
-
Multi-instance pools make most sense as part of a collaboration of pools because the relationship with the "parent" is visible
-
With interrupting boundary events, all instances will be aborted